The coronavirus pandemic has triggered a crisis in the global tourism industry with border closures and lockdowns resulting in global air traffic falling 60.8% in April year-on-year. The International Air Transport Association (IATA) is suggesting the pandemic could cost the airline industry $314 billion.
In 2018, international arrivals to MENA destinations grew by 10% and for a number of countries, tourism is an increasingly important source of employment. In oil-based economies, such as Saudi Arabia, tourism is a key component of plans to diversify revenue streams. 2019 was an excellent year for tourism, with the region outpacing the global average in competitive growth.
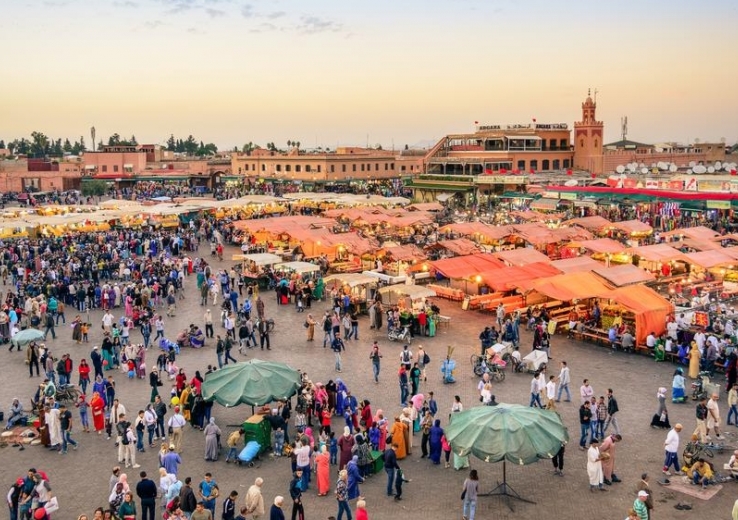
Within the MENA, countries in North Africa, most notably Egypt, Morocco, and Tunisia, stand out for their high tourist numbers. In 2019, a record 13 million tourists visited Morocco, an increase of 5.2.% compared to the year before while Egypt saw an increase of 21%, welcoming just under 14 million tourists.
The impact of coronavirus in the MENA region
Tourism represents a greater share of regional GDP than in the world’s other four travel regions (Europe and Eurasia, Asia-Pacific, the Americas, and Sub-Saharan Africa), highlighting the threat that shutting down travel represents to regional prosperity in the MENA.
In the first quarter of 2020, Tunisia recorded a 27% decrease in tourism revenues. Tourism represents the second biggest contributor to the country’s GDP. When the pandemic hit, the sector was already in recovery following sustained damage in the aftermath of the 2015 terrorist attacks that targeted Sousse, a popular tourist destination.
What will tourism look like after coronavirus?
With summer approaching and the reopening of international borders across Europe, many are beginning to look ahead to where their next trip may take them. The novel coronavirus remains highly contagious, as new outbreaks in factories and following large gatherings continue to demonstrate, and will undoubtedly have implications on tourism for some time to come.
In May, the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) issued a set of guidelines to assist the tourism sector as it emerges from the COVID-19 crisis. Central to the guidelines is the development of safety protocols. Suggestions for ensuring traveller safety include immunization certificates, mandatory testing at airports, increased frequency of cleaning, and measures to implement social distancing at airports and on planes.
Despite the disruption of the past few months and the challenges ahead, officials in Dubai remain confident that the Emirati state will be able to attract large numbers of tourists in the near future. Citing high numbers of online activity and enquiries, officials claimed Dubai could become a “top five” tourist destination. Last month Dubai began to slowly reopen hotels and beaches while spas, pools, and children’s play areas remain closed.
In Tunisia, industry leaders are urging officials to consider diversifying the country’s tourism offerings. The large, resort-based, all-inclusive offerings that are popular in Tunisia will be difficult to modify to COVID-19 requirements. Suggested alternatives include developing tourism for more upscale clientele with a focus on boutique hotels and personalized services.